Golf vs API Gateways for MCP Security: Q4 2025 Comparison
Explore why Golf's protocol-aware firewall outperforms API gateways for MCP security, addressing vulnerabilities and enhancing observability.

Golf vs API Gateways for MCP Security: Q4 2025 Comparison
API gateways handle MCP traffic as opaque HTTP payloads, missing critical security context like JSON-RPC semantics, tool schemas, and session states that define Model Context Protocol operations. Golf's protocol-aware firewall inspects these MCP-specific elements, enabling OAuth 2.1 token validation per tool invocation and detecting tool poisoning attacks that generic gateways cannot identify.
At a Glance
• Traditional API gateways lack JSON-RPC parsing and tool schema validation required for MCP security
• Over 70% of MCP implementations contain critical vulnerabilities due to missing protocol awareness
• Golf runs entirely within your VPC as a Docker container or Kubernetes sidecar, ensuring data never leaves your infrastructure
• Protocol-aware inspection detects tool poisoning, rug pulls, and cross-server shadowing attacks that bypass generic rate limiting
• OAuth 2.1 with relationship-based access control (ReBAC) enforces fine-grained permissions at the tool-invocation level
• Structured audit logs meet HIPAA and OMB M-21-31 compliance requirements that HTTP logs cannot satisfy
The agentic internet is accelerating faster than most security teams anticipated. By late 2025, enterprises are racing to deploy AI agents that autonomously call tools, query databases, and orchestrate workflows across distributed systems. Yet a hard lesson keeps surfacing: MCP security hinges on protocol-aware controls, not generic traffic gates. Traditional API gateways throttle requests and route packets, but they remain blind to the JSON-RPC semantics, tool schemas, and session context that define Model Context Protocol traffic.
This comparison examines why Golf's protocol-aware firewall outclasses mainstream gateways for MCP workloads, where legacy throttling and logging fall short, and how OAuth 2.1 plus relationship-based access control close gaps that rate limiting alone cannot address.
Why MCP Security Demands Protocol Awareness
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a framework designed to facilitate communication between AI applications and external tools, data sources, and workflows. Unlike REST endpoints that follow predictable CRUD patterns, MCP uses JSON-RPC 2.0 over multiple transports, maintains stateful sessions, and exposes dynamic tool registries that agents discover at runtime.
"Without proper protocol awareness, MCP implementations are susceptible to various attack vectors, compromising system integrity," notes a Security Boulevard analysis of common deployment failures. The core problem is structural: MCP sessions carry context that generic gateways never parse.
Security researchers have documented alarming prevalence rates. "MCP's lack of protocol awareness can lead to significant security gaps," according to a Strobes vulnerability study. The same report found that over 70% of MCP implementations have at least one critical vulnerability.
Docker's infrastructure team reinforces the point with production data: over 70% of AI infrastructure breaches are linked to protocol vulnerabilities, including those in MCP. When gateways treat MCP traffic as opaque HTTP payloads, they miss tool-poisoning payloads, session-hijacking attempts, and unauthorized tool invocations entirely.
Key takeaway: Protocol awareness is not a feature; it is the foundation of MCP security. Without it, every defense layer downstream operates on incomplete information.
Golf's Protocol-Aware Layer: How Is It Different?
Golf is the localized firewall that inspects, sanitizes, and logs every agent tool call, deployed entirely within your VPC. Unlike cloud-proxied solutions, Golf runs as a high-performance Docker container or Kubernetes sidecar, ensuring nothing leaves your infrastructure.
Traditional API gateways struggle with MCP because they were built for stateless request-response cycles. MCP, by contrast, is a session-oriented standard enabling AI agents to maintain persistent, context-rich dialogues with backend services. An API7 architecture guide explains that "MCP Gateways solve the Achilles' heel of AI systems: maintaining context across distributed interactions."
Golf addresses this with several protocol-aware capabilities:
| Capability | Golf | Generic API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| JSON-RPC method inspection | Yes | No |
| Tool schema validation | Yes | No |
| Per-session JWT enforcement | Yes | Limited |
| OAuth 2.1 scope binding | Native | Partial |
| PII redaction before LLM context | Yes | No |
| SIEM integration (Sentinel, Splunk) | Structured logs | Raw HTTP logs |
The MCP Gateway specification notes that protocol-aware gateways support observability that allows for better monitoring and management of MCP traffic. Golf extends this by integrating with Okta and Azure to map every agent interaction to a specific human identity, enforcing strict RBAC policies on a per-tool basis.
Organizations already running Golf report tangible improvements. MCP Gateways with session-aware routing report 50% fewer connectivity-related incidents and 30% lower latency for stateful workflows compared to generic proxies.
As one enterprise security lead stated, "Golf provided the secure gateway and the architectural assurance that made our high standards for security and customer trust a reality."
Where Do Traditional API Gateways Fall Short?
API gateways excel at routing, caching, and rate limiting. However, MCP workloads expose three blind spots that generic gateways cannot address.
1. Protocol Opacity
Azure API Management explicitly states: "API Management currently supports MCP server tools, but it doesn't support MCP resources or prompts." This partial coverage leaves prompts, the primary vector for injection attacks, unmonitored.
2. Fixed Quotas
Amazon API Gateway enforces a throttle quota of 10,000 requests per second with burst capacity managed by the token bucket algorithm. While effective against volumetric floods, these limits ignore the semantic content of requests. A single malicious tool call consumes the same quota as a benign health check.
3. Connection Limits
Oracle API Gateway documentation lists a maximum number of simultaneous HTTPS connections from a single IP address. AI agents frequently multiplex sessions, causing legitimate traffic to hit these ceilings while attackers spread requests across IP ranges.
The Throttling Ceiling
Throttling settings in API Gateway are applied in a strict hierarchy: account-level throttling per Region, API stage-level throttling, then method-level throttling. Each layer operates on request counts, not request intent.
The AWS Well-Architected Framework warns that leaving API endpoint throttles at default values without considering expected volumes is a common anti-pattern. For AI workloads, the anti-pattern is more fundamental: throttling stops volumetric floods but not context-aware attacks.
Rate limiting is a technique used to control the amount of incoming or outgoing traffic to or from a network. It does not inspect payloads, validate tool schemas, or detect anomalous LLM request patterns. When agents invoke tools at scale, fixed quotas bottleneck legitimate automation while attackers craft low-volume, high-impact payloads that slip under the ceiling.
Key takeaway: Throttling protects infrastructure from overload; it does not protect data from exfiltration or systems from unauthorized actions.
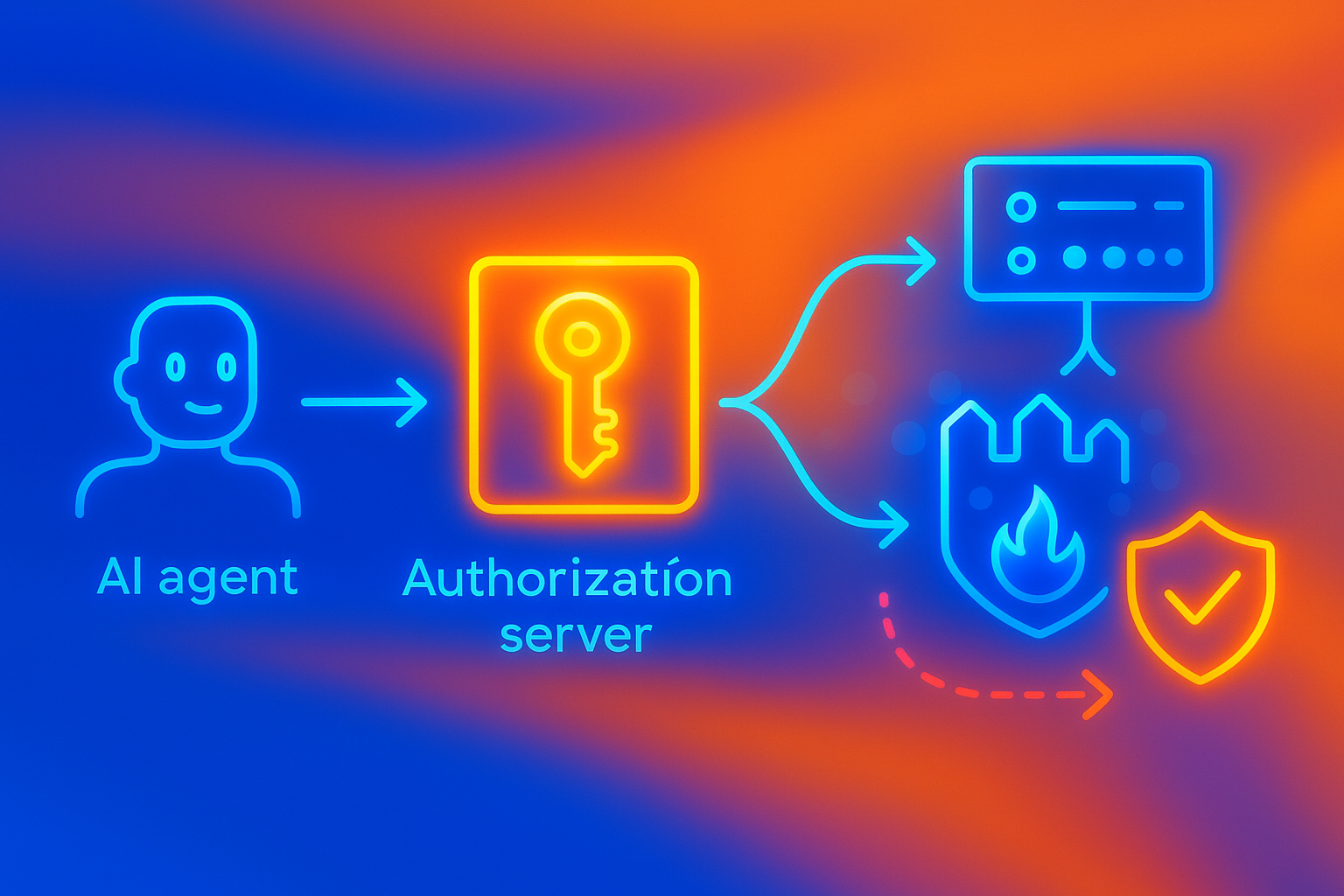
How Does OAuth 2.1 Enable Fine-Grained Authorization for MCP?
As AI agents grow more capable and access more systems with the help of MCP servers, the question of security becomes crucial. MCP now relies on OAuth 2.1, the same protocol that secures much of the modern web.
OAuth 2.0 plays a pivotal role in securing MCP servers by providing a standardized framework for authentication and authorization. OAuth 2.1 consolidates best practices: mandatory PKCE for public clients, short-lived tokens, and scoped permissions that adhere to the principle of least privilege.
Key authorization server requirements include:
- Authorization Code Flow with PKCE: Prevents interception of authorization codes.
- Dynamic Client Registration: Enables new AI agents to onboard without manual administrative intervention.
- Fine-grained scopes and claims: Restricts each token to specific tools and resources.
Golf implements OAuth 2.1 natively, binding every tool invocation to a validated token. This five-stage authentication and authorization process links user, agent, MCP server, and downstream service identities into a single auditable chain.
Relationship-Based Access & Human-in-Loop Controls
Role-based access control (RBAC) maps roles to permissions, but agentic workflows demand more granularity. Relationship-based access control (ReBAC), inspired by Google Zanzibar, captures true user-agent-resource relationships.
For high-risk operations, human-in-the-loop (HITL) approvals add a safety net. Organizations can add break-glass approvals as another policy clause, requiring manual confirmation before sensitive tool invocations proceed.
Permit.io's MCPermit architecture illustrates the pattern: unified policy across users, agents, and tools with complete visibility and auditing. Traditional API gateways and IAM tools were never designed for autonomous, context-driven agents; MCPermit authenticates, authorizes, and audits every interaction.
Key takeaway: OAuth 2.1 plus ReBAC plus HITL controls create layered authorization that adapts to agentic workflows, a capability absent from generic gateways.
How Do You Defend Against Tool Poisoning & Prompt Injection?
The Vulnerable MCP Project catalogs high-risk exploits including tool poisoning attacks where malicious instructions hide in tool descriptions, rug pulls where tools silently redefine themselves, and cross-server tool shadowing.
An indirect prompt injection vulnerability is a security exploit targeting generative AI systems where malicious instructions are embedded in external content, such as documents, web pages, or emails. When agents process these sources, hidden prompts hijack behavior.
Palo Alto Networks Unit42 researchers documented critical MCP sampling vulnerabilities: resource theft, conversation hijacking, and covert tool invocation all exploit the protocol's implicit trust model and lack of robust security controls.
AI Prompt Shields in Practice
Microsoft developed AI Prompt Shields to defend against both direct and indirect prompt injection attacks. These shields use machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to detect and filter out malicious instructions embedded in external content.
Microsoft continuously monitors and updates Prompt Shields to address new and evolving threats. The approach serves as a blueprint for enterprise deployments.
The Model Context Protocol Security project notes that indirect prompt injection involves malicious instructions embedded in external data sources such as emails, documents, and web content, causing AI systems to perform unintended actions without direct user input manipulation. Mitigation strategies include content filtering, processing controls, and behavioral monitoring.
Golf integrates similar detection layers. The AI Firewall scans inputs and outputs in real-time, detecting "Ignore previous instructions" patterns and redacting PII before data returns to the LLM context.
Why Are Audit Trails Essential Beyond Rate Limiting?
Rate limiting stops volumetric attacks; audit trails solve accountability. Regulations like HIPAA and OMB M-21-31 demand more than request counts.
CMS retains logs online for 12 months and archives them for an additional 18 months, ensuring access to audit trails for investigations. M-21-31 establishes federal standards for logging, retention, and access controls to improve cybersecurity incident investigation and response.
Stanford's HIPAA Security policy mandates that systems implement automated or procedural audit logging that supports individual accountability, reconstruction of events, intrusion detection, and other problem identification. This level of detail, capturing who created, accessed, modified, or deleted electronic protected health information, requires protocol-aware logging.
The Phase 2 HIPAA Audit Program reviews policies and procedures adopted by covered entities and business associates to meet Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules. Generic gateway logs, which capture HTTP status codes and request durations, fall short of these requirements.
Golf pipes structured logs of every tool call directly to Microsoft Sentinel and Splunk. Logs capture session IDs, JSON-RPC method calls, payloads, latencies, and errors, enabling compliance teams to reconstruct agent behavior at the tool-invocation level.
Key takeaway: Compliance frameworks require user-level, action-level logging. Protocol-aware audit trails meet M-21-31 and HIPAA-AU mandates; HTTP logs do not.
Decision Matrix: Q4 2025 Landscape of Protocol-Aware Controls
The security service edge market is a dynamic space focused on consolidating cloud-delivered point solutions and replacing or augmenting legacy hardware. Gartner's Magic Quadrant categorizes vendors into Leaders, Visionaries, Niche Players, and Challengers based on execution and vision.
Forrester's Multicloud Container Platforms Landscape notes that cloud leaders should understand the value they can expect from MCP vendors, learn how vendors differ, and investigate options based on size and market focus. Differentiation increasingly hinges on protocol awareness, not generic gateway features.
Secure access service edge (SASE) is an emerging technology that combines networking and security in a cloud-based solution. Forrester projects a five-year-plus horizon for maximum return as solutions advance to address more complex scenarios, including agentic workloads.
| Criterion | Golf | Traditional API Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol-aware inspection | Native JSON-RPC parsing | None |
| OAuth 2.1 + PKCE + ReBAC | Integrated | Partial or manual |
| Human-in-the-loop approvals | Built-in policy clauses | External orchestration |
| Prompt injection detection | AI Firewall | Not supported |
| Compliance-grade audit logs | Structured, 12+ month retention | HTTP logs only |
| Deployment | VPC sidecar, no egress | Cloud proxy or edge |
For AppSec leads and CISOs at data-sensitive enterprises, the decision matrix reveals a clear pattern: protocol-aware controls close the gaps that throttling and generic logging leave open.
Build Protocol Awareness Now - Or Pay the Security Tax Later
Every MCP server and direct database connection creates a blind spot in your security posture. Generic API gateways were designed for a stateless, human-initiated request model. Agentic AI operates differently: autonomous, context-driven, and session-aware.
Golf provided the secure gateway and the architectural assurance that made high standards for security and customer trust a reality for early adopters. Organizations that delay protocol-aware controls accumulate technical debt in compliance gaps, incident response delays, and unquantified data-leakage risk.
Action: Deploy a protocol-aware firewall now. Map every agent interaction to a human identity. Log every tool invocation at the semantic level. The security tax compounds; the investment in protocol awareness pays dividends immediately.
For teams building internal MCP factories or embedding agentic features into products, Golf delivers the intent-driven, protocol-aware observability that generic gateways cannot match. Start with a single-workflow MCP server, validate the architecture, and scale confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is MCP and why is protocol awareness important?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a framework for AI applications to communicate with external tools and data sources. Protocol awareness is crucial because it ensures that security measures can understand and manage the specific semantics and context of MCP traffic, preventing vulnerabilities that generic API gateways might miss.
How does Golf's protocol-aware firewall differ from traditional API gateways?
Golf's firewall inspects, sanitizes, and logs every agent tool call within your VPC, unlike traditional API gateways that handle stateless requests. It offers JSON-RPC method inspection, tool schema validation, and OAuth 2.1 integration, providing a more secure and context-aware solution for MCP workloads.
What are the limitations of traditional API gateways for MCP security?
Traditional API gateways are limited by their inability to parse MCP-specific traffic, relying on generic throttling and logging. They fail to address protocol opacity, fixed quotas, and connection limits, which can leave MCP systems vulnerable to context-aware attacks.
How does OAuth 2.1 enhance security for MCP servers?
OAuth 2.1 enhances MCP server security by providing a standardized framework for authentication and authorization, including features like PKCE, short-lived tokens, and fine-grained scopes. This ensures that each tool invocation is securely bound to a validated token, reducing unauthorized access risks.
Why are audit trails essential for MCP security beyond rate limiting?
Audit trails provide detailed logs of user-level and action-level activities, essential for compliance with regulations like HIPAA and M-21-31. They enable accountability and detailed event reconstruction, which generic HTTP logs from traditional gateways cannot offer.
Sources
- https://workos.com/blog/mcp-auth-developer-guide
- https://vulnerablemcp.info/
- https://securityboulevard.com/2025/06/mcp-model-context-protocol-and-its-critical-vulnerabilities/
- https://strobes.co/blog/mcp-model-context-protocol-and-its-critical-vulnerabilities/
- https://www.docker.com/blog/mcp-security-issues-threatening-ai-infrastructure/
- https://api7.ai/ko/blog/understanding-mcp-gateway
- https://api7.ai/ar/blog/understanding-mcp-gateway
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/api-management/expose-existing-mcp-server
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/limits.html
- https://docs.oracle.com/iaas/Content/APIGateway/Reference/apigatewaylimits.htm
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/api-gateway-request-throttling.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/en_en/wellarchitected/latest/framework/rel_mitigate_interaction_failure_throttle_requests.html
- https://dev.to/colinmcdermott/api-rate-limiting-cheat-sheet-409f
- https://developer.pingidentity.com/identity-for-ai/agents/idai-securing-mcp-servers.html
- https://docs.permit.io/mcp-permissions/architecture/
- https://docs.identitymachines.com/docs/mcp-tooling-control-for-devs
- https://docs.permit.io/mcp-permissions/overview/
- https://developer.microsoft.com/blog/protecting-against-indirect-injection-attacks-mcp
- https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/model-context-protocol-attack-vectors/?pdf=print&lg=en&_wpnonce=89496ed46e
- https://devblogs.microsoft.com/blog/protecting-against-indirect-injection-attacks-mcp
- https://modelcontextprotocol-security.io/ttps/prompt-injection/indirect-prompt-injection/
- https://security.cms.gov/policy-guidance/audit-and-accountability-au-handbook
- https://uit.stanford.edu/security/hipaa/audit-controls-policy
- https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/compliance-enforcement/audit/protocol/index.html
- https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/5352963
- https://www.forrester.com/report/the-multicloud-container-platforms-landscape-q1-2025/RES182183
- https://www.forrester.com/report/the-state-of-secure-access-service-edge-2025/RES180798
